计算机网络自顶向下: Socket Programming Assignment + Miscellaneous Labs
Programming Tasks Of Computer-Networking-A-TopDown-Approach
1 lab0 WarmUp
1.1. UDP
from socket import*
serverName = '127.0.0.1' # ip or hostname , if is hostname,automatically carry out DNS lookup to find correspond ip
serverPort = 12000 # designate destination port number
clientSocket = socket(AF_INET,SOCK_DGRAM);# create client socket(ipv4,udp), clientPort is automatically allocated by OS
message = input('Input lowercase sentence:')
# message content and destination address(server_ip,server_ port),the clientAddress automatically add to the message by OS
clientSocket.sendto(message.encode(),(serverName,serverPort))
modifiedMessage, serverAddress = clientSocket.recvfrom(2048); # receive from server, 2048 is cache length
print(modifiedMessage.decode())
clientSocket.close()from socket import*
serverPort = 12000 # allocate server port number manually
serverSocket = socket(AF_INET,SOCK_DGRAM)# create server Socket(ipv4,udp)
serverSocket.bind(('',serverPort));# bind socket and port number, one socket one port number
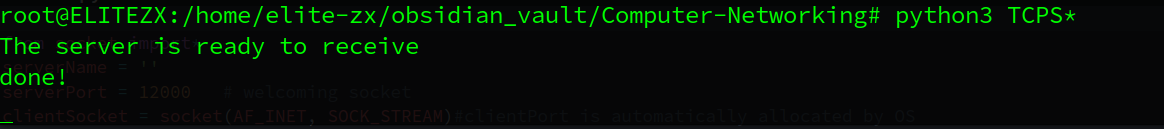
print("The server is ready to receive")
while True:
message,clientAddress = serverSocket.recvfrom(2048) # receive message from client
modifiedMessage = message.decode().upper()
print("done!")
serverSocket.sendto(modifiedMessage.encode(),clientAddress)- result

1.2. TCP
from socket import*
serverName = '127.0.0.1' # local host
serverPort = 12000 # welcoming socket
clientSocket = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM)#clientPort is automatically allocated by OS
# knock at the welcoming door(welcomingsocket),this will initiate tcp three-way handshakes
clientSocket.connect((serverName,serverPort))
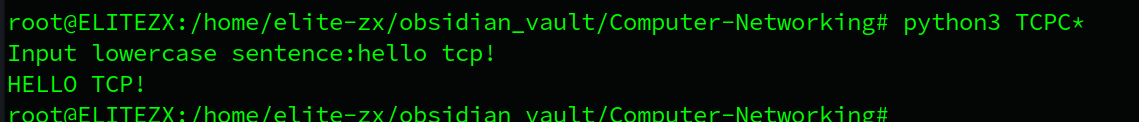
sentence=input('Input lowercase sentence:')
clientSocket.send(sentence.encode()) # send message without server addree,since tcp connection is built
modifiedSentence = clientSocket.recv(1024)
print(modifiedSentence.decode())
clientSocket.close()from socket import*
serverPort = 12000 # welcoming socket
serverSocket = socket(AF_INET,SOCK_STREAM)
serverSocket.bind(('',serverPort))
serverSocket.listen(1) # maximal connection number(at least 1)
print('The server is ready to receive')
while True:
connectionSocket, addr = serverSocket.accept() # create a new socket(connectionSocket) which is delicated to client
sentence = connectionSocket.recv(1024).decode() # receive message from connectionSocket
capitalizedSentence = sentence.upper()
print("done!")
connectionSocket.send(capitalizedSentence.encode())
connectionSocket.close()- result
lab1 Web-Server
2.1. Web-Server.py
#import socket module
from socket import *
import sys # In order to terminate the program
serverSocket = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM)
#Prepare a sever socket
#Fill in start
serverPort = 80 # allocate server port number manually
serverSocket.bind(('',serverPort))
serverSocket.listen(10) # maximal connection number
#Fill in end
while True:
#Establish the connection
print('Ready to serve...')
#Fill in start
connectionSocket, addr = serverSocket.accept() ## create a new socket(connectionSocket) which is delicated to client
#Fill in end
try:
#Fill in start
message = connectionSocket.recv(1024); # receive message from connectionSocket
#Fill in end
filename = message.split()[1] # get filename from string list message
f = open(filename[1:])
#Fill in start
outputdata = f.read()
#Fill in end
#Send one HTTP header line into socket
#Fill in start
header = 'HTTP/1.1 200 OK\r\nConnection: close\r\nDate: Tue, 23 May 2023 11:14:01 GMT\r\nContent-Type: text/html\r\nContent-Length: %d\r\n\r\n' % (len(outputdata)) # Comply with the HTTP response message format
connectionSocket.send(header.encode())
#Fill in end
#Send the content of the requested file to the client
for i in range(0, len(outputdata)):
connectionSocket.send(outputdata[i].encode())
connectionSocket.send("\r\n".encode())
connectionSocket.close()
except IOError:
#Send response message for file not found
#Fill in start
header = 'HTTP/1.1 404 Not Found'
connectionSocket.send(header.encode())
#Fill in end
#Close client socket
#Fill in start
#Fill in end
serverSocket.close()
#Fill in end
serverSocket.close()
sys.exit()#Terminate the program after sending the corresponding data
使用以下命令可以检查端口号80是否被占用
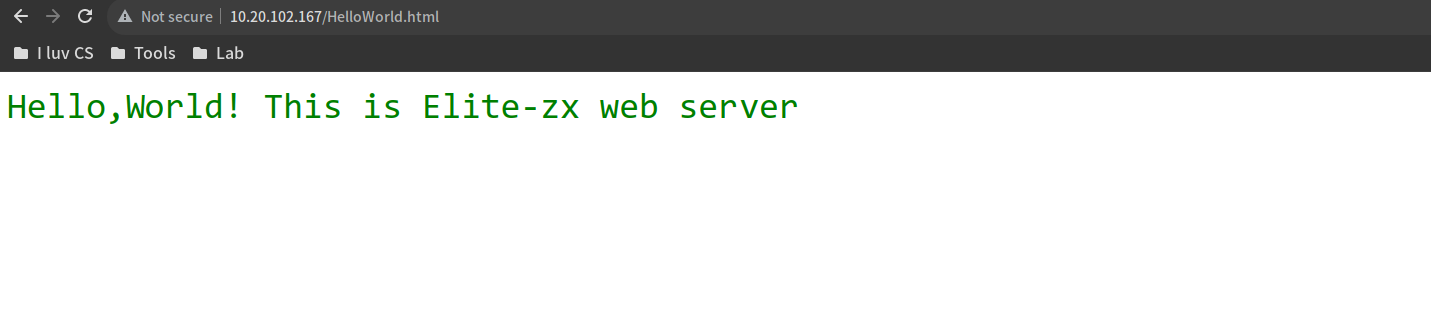
netstat -tuln | grep :8080HelloWorld.html放在Web-Server.py同目录下,内容如下:
<span style="color: green; font-size: 36px;">Hello,World! This is Elite-zx web server</span>2.2. result
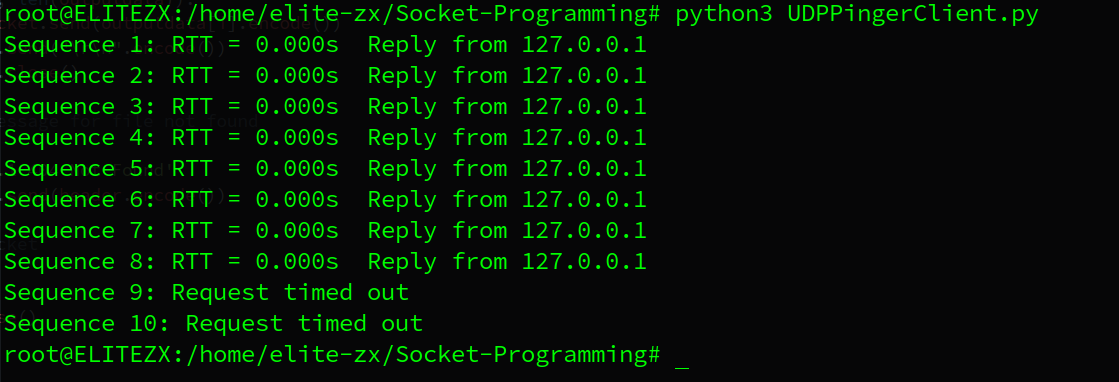
lab3 UDPPinger
3.1. UDPPingerClient.py
from socket import*
import time
serverName = '127.0.0.1'
serverPort = 12000
clientSocket = socket(AF_INET,SOCK_DGRAM);
clientSocket.settimeout(1) # timeout is 1 second
for i in range(0,10):
sendTime = time.time()
message =('Ping %d %s' % (i+1,sendTime)).encode()
try:
clientSocket.sendto(message,(serverName,serverPort))
modifiedMessage, serverAddress = clientSocket.recvfrom(2048)
rtt = time.time() - sendTime
print('Sequence %d: RTT = %.3fs Reply from %s' % (i+1,rtt,serverName))
except Exception: # time out Exception, socket.timeout is not from BaseException
print('Sequence %d: Request timed out' % (i+1))
clientSocket.close()3.2. UDPPingerServer.py
# We will need the following module to generate randomized lost packets
import random
from socket import *
# Create a UDP socket
# Notice the use of SOCK_DGRAM for UDP packets
serverSocket = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_DGRAM)
# Assign IP address and port number to socket
serverSocket.bind(('', 12000))
while True:
# Generate random number in the range of 0 to 10
rand = random.randint(0, 10)
# Receive the client packet along with the address it is coming from
message, address = serverSocket.recvfrom(1024)
# Capitalize the message from the client
message = message.upper()# If rand is less is than 4, we consider the packet lost and do not respond
if rand < 4:
continue
# Otherwise, the server responds
serverSocket.sendto(message, address)3.3. result
lab4 SMTP-Client
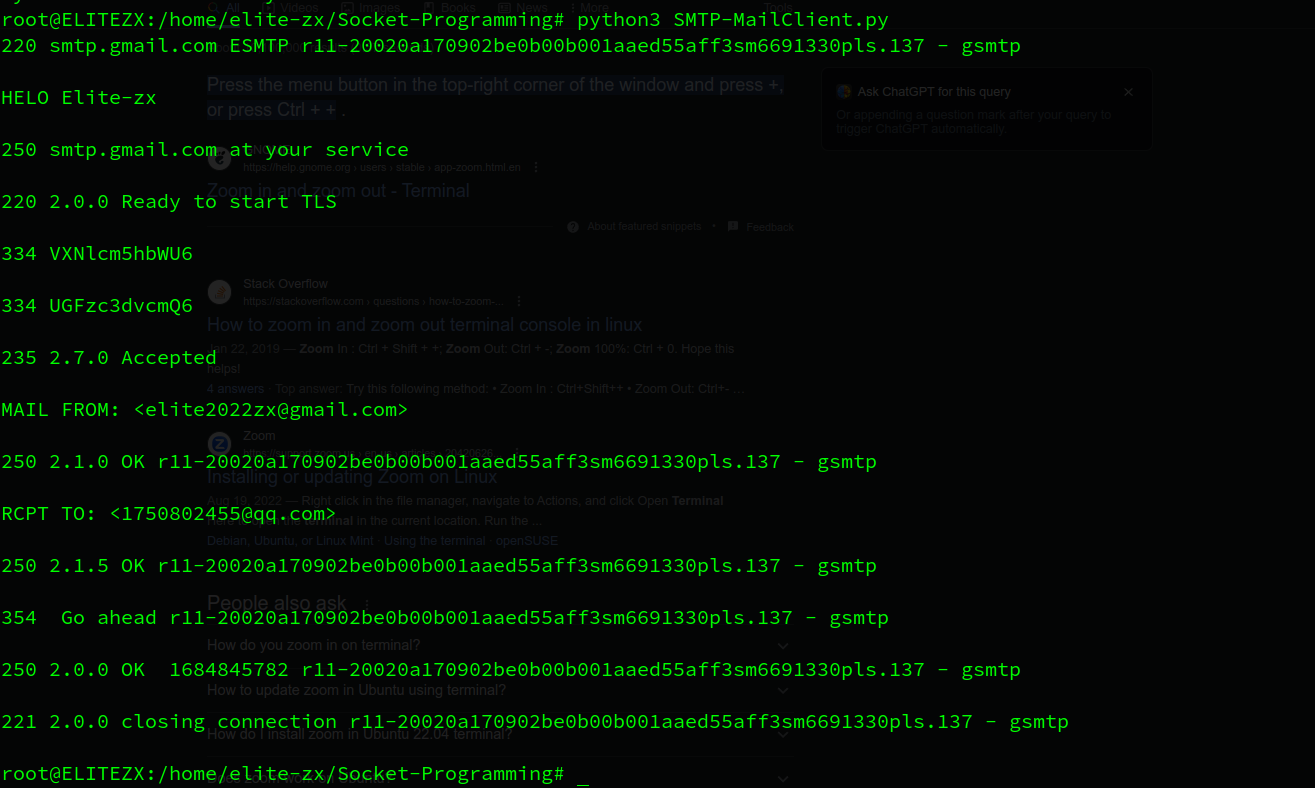
4.1. SMTP-MailClient.py
这里访问的是Gmail的服务器,因此多了2个额外的步骤
- 建立TLS (Transport Layer Security) 连接,为了加密
- 在Google账户中开启双重验证,为Gmail设置单独的密码,直接用Google账户的密码AUTH LOGIN,Gmail服务器不认的,会返回
535-5.7.8 Username and Password not accepted。如果账户密码正确,则返回235 2.7.0 Accepted
注意账户密码使用base64编码,这可以通过base64.b64encode函数做到
from socket import *
import base64
import ssl
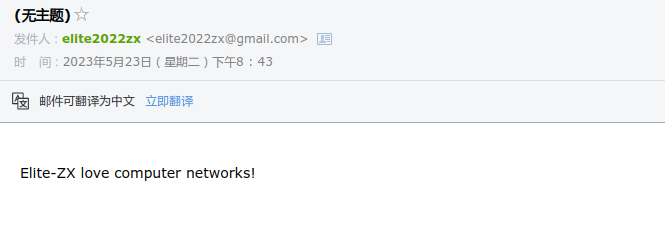
msg = "\r\n Elite-ZX love computer networks!"
endmsg = "\r\n.\r\n"
# Choose a mail server (e.g. Google mail server) and call it mailserver
#Fill in start
mailServer = 'smtp.gmail.com'
mailPort = 587
fromAddress = '********@gmail.com'
toAddress = '********@qq.com'
username = base64.b64encode(b'********@gmail.com').decode()
password = base64.b64encode(b'********').decode()
#Fill in end
# Create socket called clientSocket and establish a TCP connection with mailserver
#Fill in start
clientSocket = socket(AF_INET,SOCK_STREAM)
clientSocket.connect((mailServer,mailPort))
#Fill in end
recv = clientSocket.recv(1024).decode()
print(recv)
if recv[:3] != '220':
print('220 reply not received from server.')
# Send HELO command and print server response.
heloCommand = 'HELO Elite-zx\r\n'
print(heloCommand)
clientSocket.send(heloCommand.encode())
recv1 = clientSocket.recv(1024).decode()
print(recv1)
if recv1[:3] != '250':
print('250 reply not received from server.')
# Send STARTTLS command and print server response
clientSocket.send(('STARTTLS\r\n').encode())
recv = clientSocket.recv(1024).decode()
print(recv)
if recv[:3] != '220':
print('220 reply not received from server.')
# Create TLS connection
context = ssl.create_default_context()
clientSocket = context.wrap_socket(clientSocket, server_hostname='smtp.gmail.com')
# Send AUTH LOGIN command
authLoginCommand='AUTH LOGIN\r\n'
clientSocket.send(authLoginCommand.encode())
recv = clientSocket.recv(1024).decode()
print(recv)
if (recv[:3] != '334'):
print('334 reply not received from server')
# Send username
clientSocket.send((username+'\r\n').encode())
recv = clientSocket.recv(1024).decode()
print(recv)
if (recv[:3] != '334'):
print('334 reply not received from server')
# Send password
clientSocket.send((password+'\r\n').encode())
recv = clientSocket.recv(1024).decode()
print(recv)
if (recv[:3] != '235'):
print('235 reply not received from server')
# Send MAIL FROM command and print server response.
# Fill in start
print('MAIL FROM: <' + fromAddress + '>\r\n')
clientSocket.send(('MAIL FROM: <' + fromAddress + '>\r\n').encode())
recv2 = clientSocket.recv(1024).decode()
print(recv2)
if recv2[:3] != '250':
print('250 reply not received from server.')
# Fill in end
# Send RCPT TO command and print server response.
# Fill in start
print('RCPT TO: <'+ toAddress + '>\r\n')
clientSocket.send(('RCPT TO: <'+ toAddress + '>\r\n').encode())
recv3 = clientSocket.recv(1024).decode()
print(recv3)
if recv3[:3] != '250':
print('250 reply not received from server.')
# Fill in end
# Send DATA command and print server response.
# Fill in start
DataCommand = 'DATA\r\n'
clientSocket.send(DataCommand.encode())
recv4 = clientSocket.recv(1024).decode()
print(recv4)
if recv4[:3] != '354':
print('354 reply not received from server.')
# Fill in end
# Send message data.
# Fill in start
clientSocket.send(msg.encode())
# Fill in end
# Message ends with a single period.
# Fill in start
clientSocket.send(endmsg.encode())
recv5 = clientSocket.recv(1024).decode()
print(recv5)
if recv5[:3] != '250':
print('250 reply not received from server.')
# Fill in end
# Send QUIT command and get server response.
# Fill in start
QuitCommand = 'QUIT\r\n'
clientSocket.send(QuitCommand.encode())
recv6 = clientSocket.recv(1024).decode()
print(recv6)
if recv6[:3] != '221':
print('221 reply not received from server.')
# Fill in end4.2. result
lab5 ProxyServer
5.1. setback road
这个实验我踩了很多坑,一来是因为文档给出的源码与python3有很多不合的地方,二来网上没有很好的参考,包括github上热度很高的那个参考对我也不可行。因此我靠着添加try-except语句,stackoverflow以及chatgpt的分析,花了一个五六个小时总算是做出来了。
下面我将列举我踩的坑
- 端口80默认绑定到http协议,因此访问https的网站将被拒绝连接。大多数网站即使你的URL是http还是会给你重定向到https,因此建议使用http://gaia.cs.umass.edu/wireshark-labs/INTRO-wireshark-file1.html进行结果测试,文档里提到的www.google.com怕是不可行吧🤨
- 关于split和partition的使用,目的是在URL中提取出源服务器gaia.cs.umass.edu和目标文件路径wireshark-labs/INTRO-wireshark-file1.html,要根据你访问的网站做调整
- send函数内的参数均要加上用encode()处理,使参数从字符流变成字节流,否则会抛出
a bytes-like object is required, not 'str'的异常 makefile()函数返回一个与socket关联的文件对象,这里应该使用fileobj = c.makefile('rw',None),则不是文档里的fileobj = c.makefile('r', 0),首先参数0是python2中的,在python3已被替换为None, 而且如果用只读模式打开,后续write将会抛出不可写入的异常fileobj.write("GET /".encode()+ filename.encode() + " HTTP/1.0\r\n\r\n".encode())的执行迟迟不结束,原来是发送的http请求先被放入了内部缓冲区等待发送,添加fileobj.flush()刷新缓冲区,立即发送请求- 一开始参考了github上的代码直接转发message即
c.sendall(message.encode()),可是浏览器总是会先发出先自动GET /favicon.ico HTTP/1.1的请求,查阅stackflow后,这个行为要修改html头部才能避免,因此只能采用文档提供的方法即自己构造HTTP请求(虽然浏览器在该请求之后还是会自动发出GET /favicon.ico HTTP/1.1请求😕) - 因为目标路径文件包含一个子目录,因此要先在代理服务器下创建一个wireshark-labs的文件夹以避免
tmpFile = open("./" + filename,"wb")抛出子目录不存在的异常)
5.2 ProxyServer.py
from socket import *
import sys
if len(sys.argv) <= 1: # get listening port
print('Usage : "python ProxyServer.py listening_port"\n[server_ip : It is the listening\
port of Proxy Server')
sys.exit(2)
# Create a server socket, bind it to a port and start listening
tcpSerSock = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM)
# Fill in start.
tcpSerPort = int(sys.argv[1])
tcpSerSock.bind(('',tcpSerPort))
tcpSerSock.listen(6)
# Fill in end.
while 1:
# Start receiving data from the client
print('Ready to serve...')
tcpCliSock, addr = tcpSerSock.accept()
print('Received a connection from: ', addr)
# Fill in start.
message = tcpCliSock.recv(2048).decode()
# Fill in end.
print("message content: " , message)
# Extract the filename from the given message
print("URL: ", message.split()[1])
filename = message.split()[1].partition("/")[2].partition("/")[2]
print("filename: " , filename)
fileExist = "false"
# print(filetouse)
try:# Check wether the file exist in the cache
f = open(filename, "r")
outputdata = f.readlines()
fileExist = "true"
print("Target file exist!")
# ProxyServer finds a cache hit and generates a response message
tcpCliSock.send("HTTP/1.0 200 OK\r\n".encode())
tcpCliSock.send("Content-Type:text/html\r\n".encode())
# Fill in start.
# send file content
for i in range(0,len(outputdata)):
tcpCliSock.send(outputdata[i].encode())
# Fill in end.
print('Read from cache')
# Error handling for file not found in cache
except IOError:
if fileExist == "false":
print("Target file no exist!")
# Create a socket on the proxyserver
# Fill in start.
c = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM)
# Fill in end.
hostn = message.split()[1].partition("/")[2].partition("/")[0].replace("www.","",1) # remove www. get hostname
print("source server host: " , hostn )
try:
# Connect to the socket to port 80
# Fill in start.
c.connect((hostn,80))
print("proxy server's socket connected to source server!")
# Fill in end.
# Create a temporary file on this socket and ask port 80
# for the file requested by the client
#print("will open fileobj!")
#try:
fileobj = c.makefile('rw',None)
#except Exception as e:
# print("Exception occurred while making file:", str(e))
print("open fileobj!")
# approach + url + version of http + empty line + empty header
try:
number = fileobj.write("GET ".encode()+ filename.encode() + " HTTP/1.0\r\n\r\n".encode())
print(number)
fileobj.flush() # Send immediately, do not wait
except Exception as e:
print("Exception occurred while writing file:", str(e))
print("requested sent to source server!")
# Read the response into buffer
# Fill in start.
#c.sendall(message.encode())
#buff = c.recv(2048)
buffer = fileobj.read()
tcpCliSock.sendall(buffer)
print("buffer is ready!")
# Fill in end.
# Create a new file in the cache for the requested file.
tmpFile = open("./" + filename,"wb")
# Fill in start.
tmpFile.write(buffer)
tmpFile.close()
# Fill in end.
except Exception as e:
print("Exception: ", str(e))
print("Illegal request")
else:
# HTTP response message for file not found
# Fill in start.
tcpCliSock.send("HTTP/1.1 404 Not Found\r\n\r\n".encode())
print('File Not Found')
# Fill in end.
# Close the client and the server sockets
tcpCliSock.close()
# Fill in start.
tcpSerSock.close()
# Fill in end.5.3.result
首次访问proxy server
http://localhost:8080/gaia.cs.umass.edu/wireshark-labs/INTRO-wireshark-file1.html
代理服务器上没有目标文件,因此它向源服务器发出请求,在得到文件后转发给client并缓存目标文件在代理服务器本地
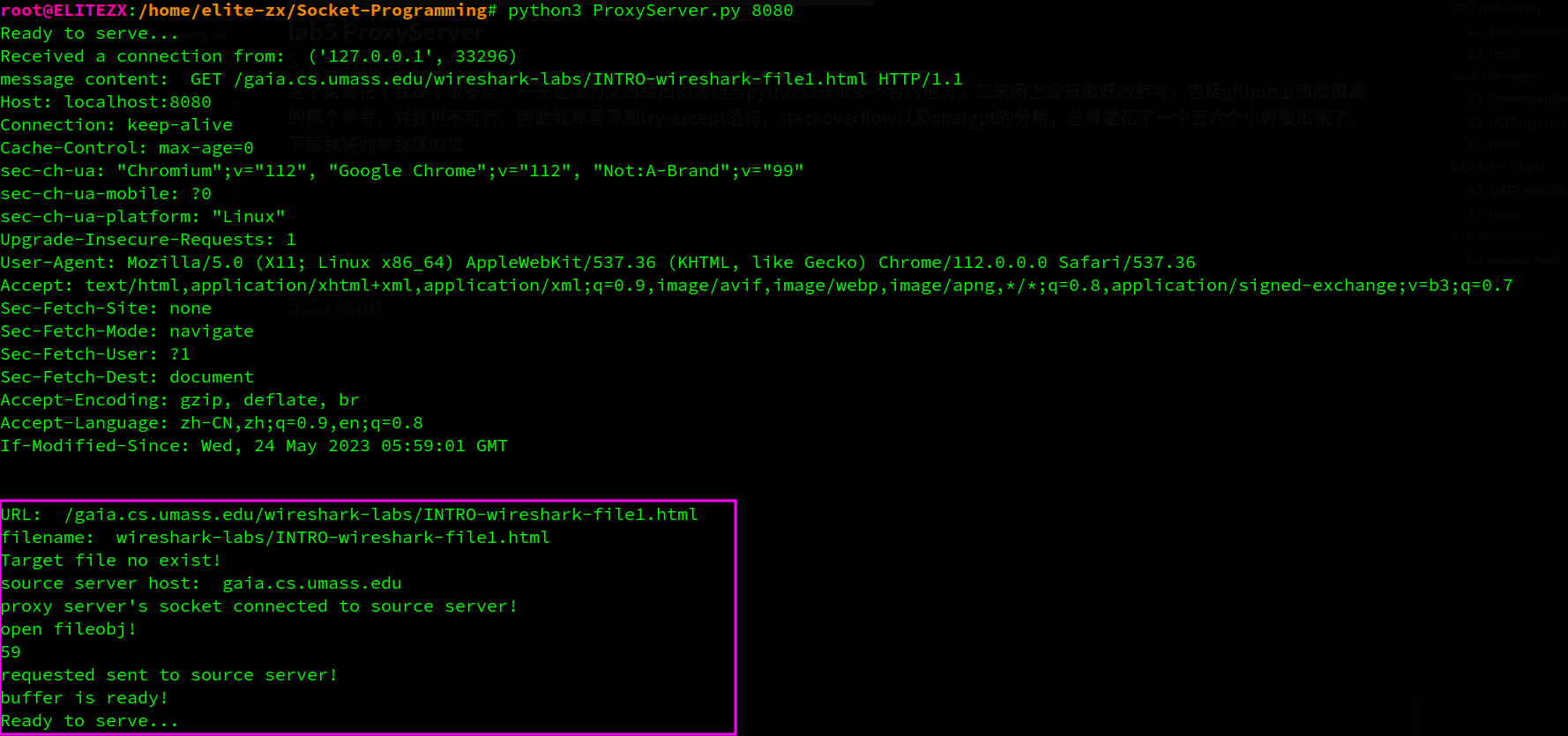
client端获取成功
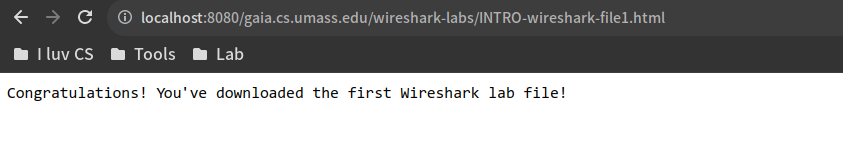
此时wireshark-labs目录下已经多了一个缓存文件
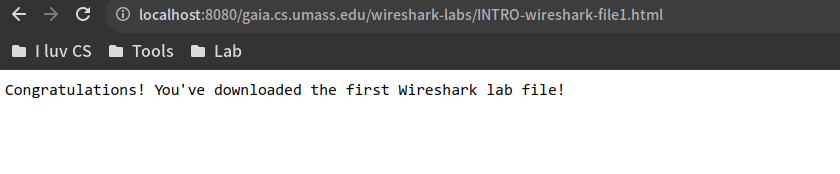
再次访问proxy server,可以看到代理服务器直接返回了已缓存的文件

client端获取成功
Reliable Transport Protocol
Tell me and I forget. Show me and I remember. Involve me and I understand.
1. Stop And Wait / Alternating-Bit
我实现的版本更像是rdt3.0,没有使用NAK,而是通过为ACK编号让接受方判断是否收到了正确的反馈信息,只要在接受方B没有收到目标packet时在ack_packet的acknum字段填入上次收到的packet序号即可。因为B反馈的ack_packet没有要求装入数据,因此ack_packet的payload字段为空,那么相应的checksum字段也不需要加上payload了,ack_packet的seqnum在该协议中没有约束。
为网络模拟器版本纠错,把exit()改成exit(0)
实验开始前,阅读文档提供的问答可以解决一些你的疑惑
1.1 analyze
发送方FSM,用A_status的4个值表示4种状态
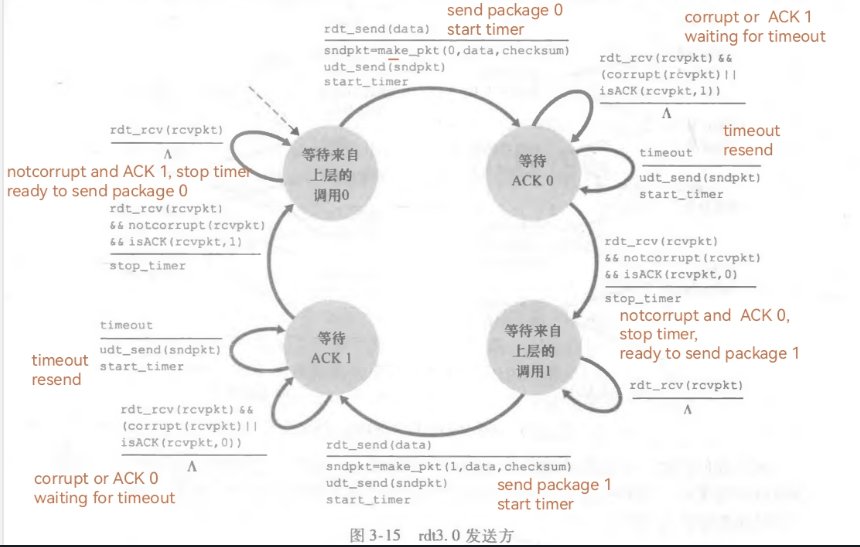
接受方的FSM,用B_status的2个值表示2种状态
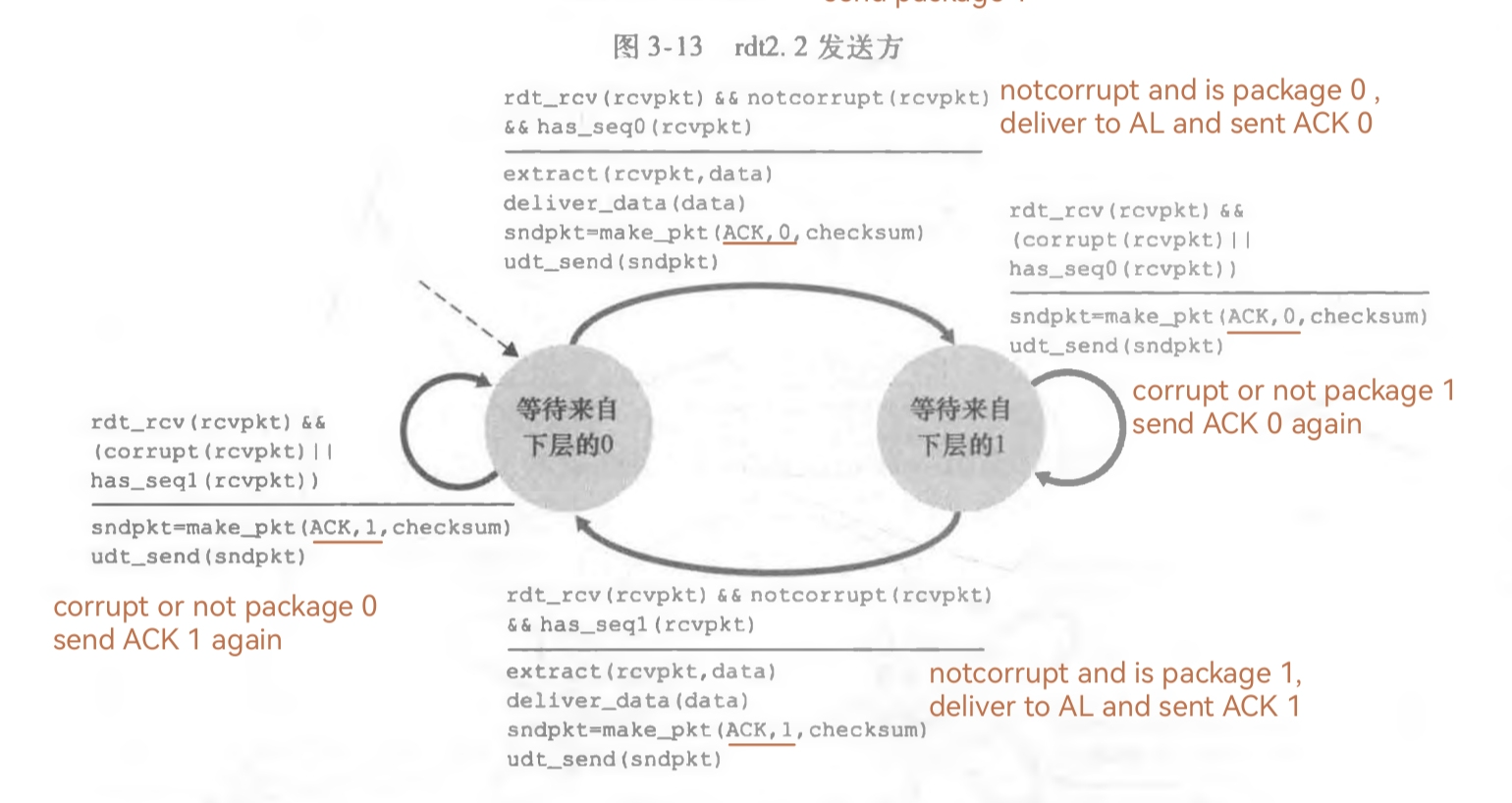
1.2. source code
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
/* ******************************************************************
ALTERNATING BIT AND GO-BACK-N NETWORK EMULATOR: VERSION 1.1 J.F.Kurose
This code should be used for PA2, unidirectional or bidirectional
data transfer protocols (from A to B. Bidirectional transfer of data
is for extra credit and is not required). Network properties:
- one way network delay averages five time units (longer if there
are other messages in the channel for GBN), but can be larger
- packets can be corrupted (either the header or the data portion)
or lost, according to user-defined probabilities
- packets will be delivered in the order in which they were sent
(although some can be lost).
**********************************************************************/
#define BIDIRECTIONAL 0 /* change to 1 if you're doing extra credit */
/* and write a routine called B_output */
int sndPkt_seq; // 0,1,0,1...
int A_status; // 4 status in FSM rdt3.0, 0 is iniital status
int B_status; // 2 status in FSM rdt2.2, waiting for packet 0 or 1
/* a "msg" is the data unit passed from layer 5 (teachers code) to layer */
/* 4 (students' code). It contains the data (characters) to be delivered */
/* to layer 5 via the students transport level protocol entities. */
struct msg {
char data[20];
};
/* a packet is the data unit passed from layer 4 (students code) to layer */
/* 3 (teachers code). Note the pre-defined packet structure, which all */
/* students must follow. */
struct pkt {
int seqnum;
int acknum;
int checksum;
char payload[20];
};
struct pkt cachedPkt;
/********* STUDENTS WRITE THE NEXT SEVEN ROUTINES *********/
/* called from layer 5, passed the data to be sent to other side */
A_output(message) struct msg message;
{
if (A_status == 1 || A_status == 3) {
printf("sender A is waiting for ACK!\n");
return -1; // waiting for ACK;
}
struct pkt sndPkt;
/*make_Pkt*/
sndPkt.seqnum = sndPkt_seq % 2;
sndPkt.acknum = -1; // not a ACKnowledged package
sndPkt.checksum = sndPkt.seqnum + sndPkt.acknum;
for (int i = 0; i < 20; ++i) sndPkt.checksum += message.data[i];
memcpy(sndPkt.payload, message.data, sizeof(message.data));
printf("A is sending packet %d !\n", sndPkt.seqnum);
/*cache_pkt*/
cachedPkt = sndPkt;
/*udt_send(sndPKt)*/
tolayer3(0, sndPkt);
/*start timer*/
starttimer(0, 12.0);
/*switch status of A*/
++A_status;
++sndPkt_seq;
}
B_output(message) /* need be completed only for extra credit */
struct msg message;
{}
/* called from layer 3, when a packet arrives for layer 4 */
A_input(packet) struct pkt packet;
{
if (A_status == 0 || A_status == 2) return -1; // incorrect status
int tmp_checksum = packet.acknum + packet.seqnum;
/*no payload of ack packet*/
/* notcorrupt and is target ACK*/
if (tmp_checksum == packet.checksum && cachedPkt.seqnum == packet.acknum) {
printf("ACK %d packet is not corrupt!\n", packet.acknum);
/* stop timer*/
stoptimer(0);
A_status = (++A_status) % 4;
} else {
printf("corrupt or not target ACK %d! will timeout and retransmit!\n",
cachedPkt.seqnum);
return -1; // corrupt or is not target ack ,waiting for timeout
}
}
/* called when A's timer goes off */
A_timerinterrupt() {
printf("sender A is retransmiting packet %d !\n", cachedPkt.seqnum);
/*udt_send*/
tolayer3(0, cachedPkt);
/*start timer*/
starttimer(0, 12.0);
}
/* the following routine will be called once (only) before any other */
/* entity A routines are called. You can use it to do any initialization */
A_init() {
sndPkt_seq = 0;
// initial status of sender A---waiting for message from layer5
A_status = 0;
}
/* Note that with simplex transfer from a-to-B, there is no B_output() */
/* called from layer 3, when a packet arrives for layer 4 at B*/
B_input(packet) struct pkt packet;
{
struct pkt ack_packet;
int tmp_checksum = packet.acknum + packet.seqnum;
for (int i = 0; i < 20; ++i) tmp_checksum += packet.payload[i];
/* notcorrupt and is target packet*/
ack_packet.seqnum = packet.seqnum;
if (tmp_checksum == packet.checksum && B_status == packet.seqnum) {
printf("notcorrupt and target packet %d! sending right ACK!\n",
packet.seqnum);
/*extract*/
struct msg extract_msg;
memcpy(extract_msg.data, packet.payload, sizeof(packet.payload));
/*deliver_data*/
tolayer5(1, extract_msg);
ack_packet.acknum = B_status;
ack_packet.checksum =
ack_packet.seqnum + ack_packet.acknum; // no payload
/*make_Pkt*/
tolayer3(1, ack_packet);
B_status = (++B_status) % 2; // switch B status
} else {
printf("corrupt or not target packet! sending last receiving ACK!\n");
ack_packet.acknum = (B_status + 1) % 2;
ack_packet.checksum =
ack_packet.seqnum + ack_packet.acknum; // no payload
tolayer3(1, ack_packet);
}
}
/* called when B's timer goes off */
B_timerinterrupt() {}
/* the following rouytine will be called once (only) before any other */
/* entity B routines are called. You can use it to do any initialization */
B_init() { B_status = 0; }1.2. result
2.1. no loss and corruption
一来一回,运行正常, packet 0与ack 0对应,packet 1与ack 1对应
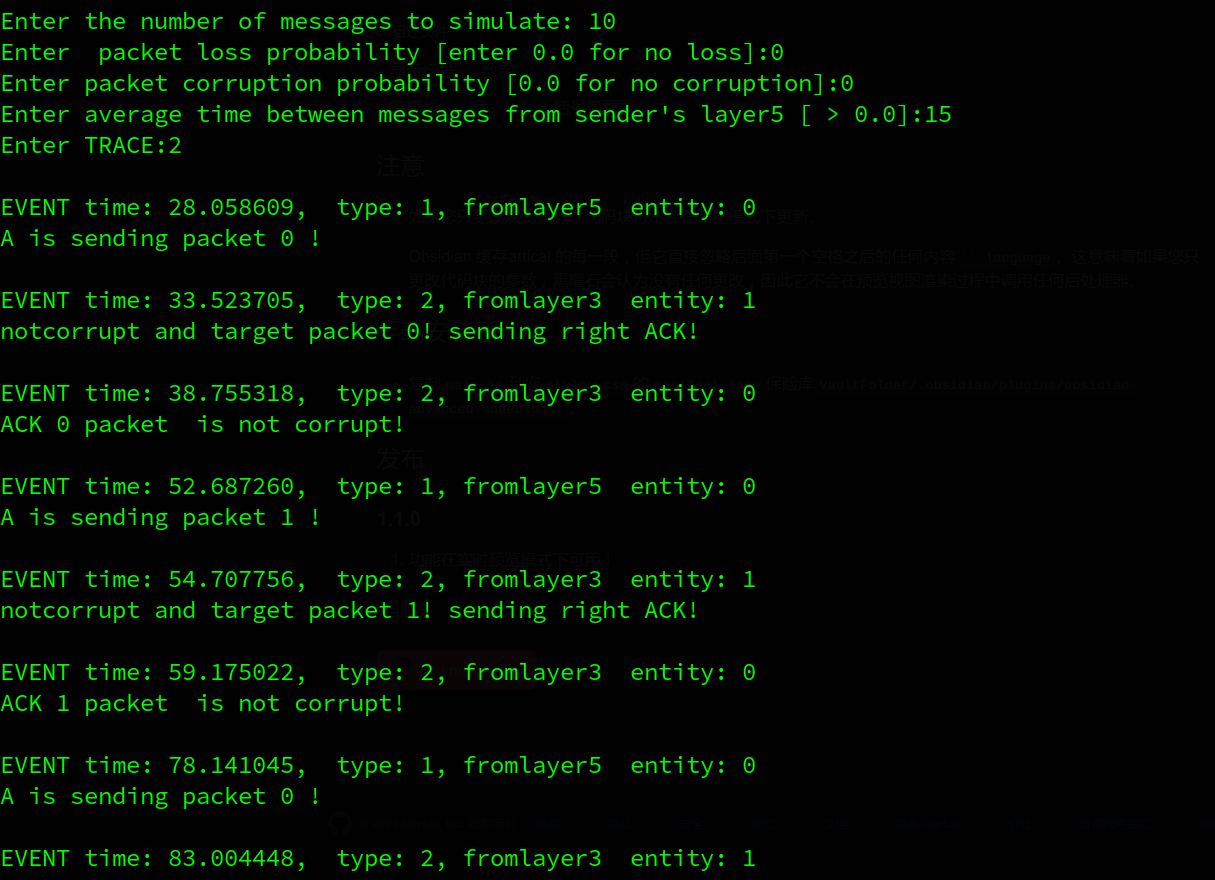
2.2 loss and corruption
虽然只设置了0.2的丢包率和损失率,但是实际上概率还是挺大的,可能是随机数生成器的问题,下面将分析部分输出来验证代码的正确性
A先发送packet0, B成功接受了packet0,但是反馈信息在layer3中被损坏,A收到损坏的ack信息后等待超时重传,重传2次的2个包都丢了,接着超时重传,发出的包又损坏了(这也太频繁了),期间A收到来自上层layer5的数据包,但是由于这是stop and wait协议,在收到发出的包的确认之前不能发送新的包,因此A只打印它在等待ack的信息。B端收到A重传的数据包,发现这不是它想要的数据包,而是冗余的数据包,因此它丢弃该包(不上传到layer5),并重新对这个序号(最后一次成功收到的序号)的包发出确认,A端收到想要的确认后,发出packet 1
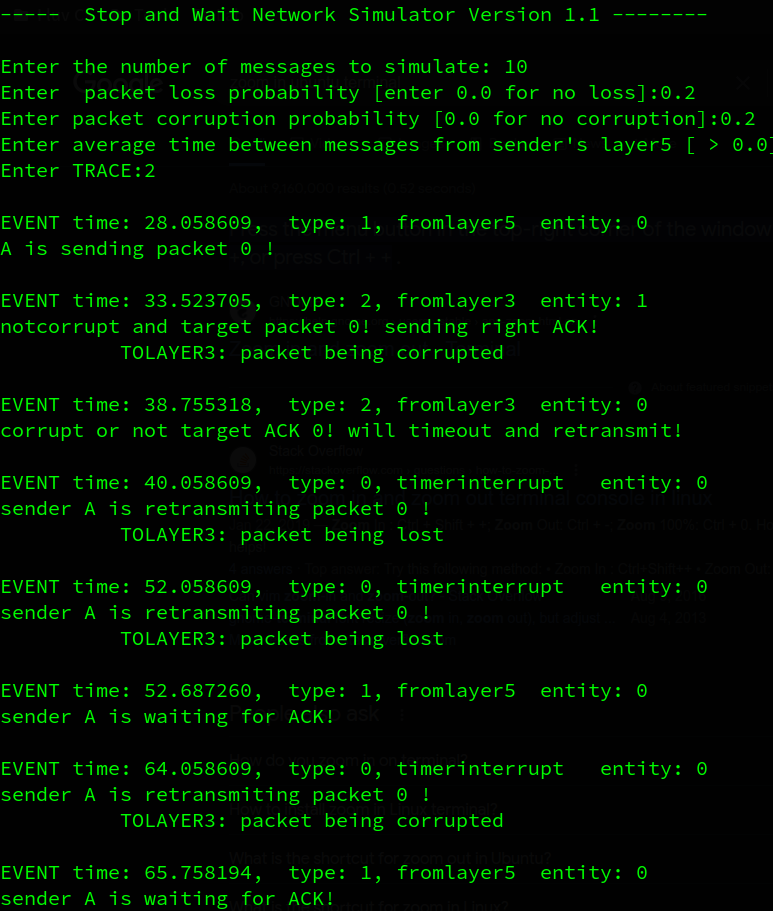
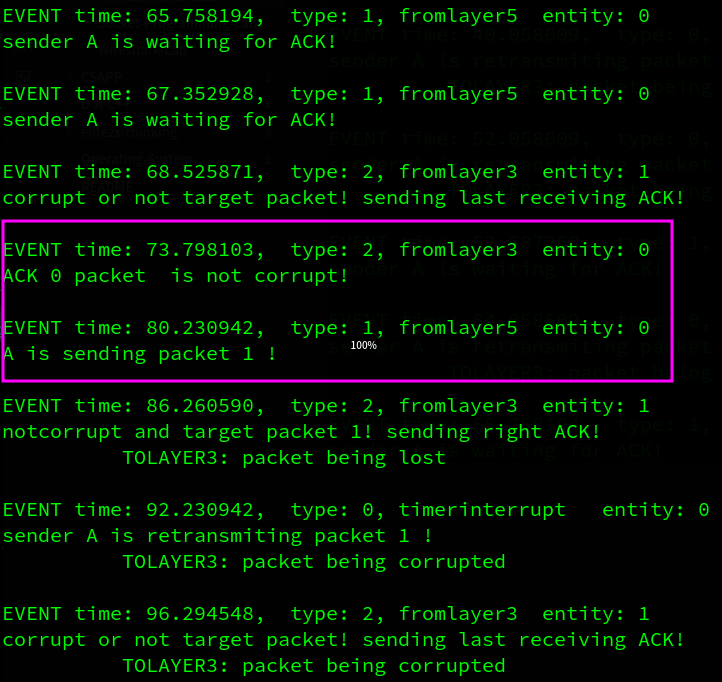

2. Go-Back-N
2.1 analyze
基于任务1, 完成GBN版本是比较轻松的,编写加调试只花了3个小时。接受方只需维护接受到最后有序packet的序号last_rcv_seq即可,在收到失序的重复的packet时发出包含last_rcv_seq的ACK即可告诉发送方自己可以确认了包含last_rcv_seq之前的所有包。因为存在ack到达之前,发送方超时重传的现象,因此发送方可能会收到冗余的ack信息,因此要设置一个acknum小于base的分支
发送方维护base和nextseq两个变量以表示window的发送边界,base表示窗口内最早发送但是未确认的序号(最右侧,窗口左移),nextseq表示下一个待发送的序号。因此当base = nextseq时,说明此时窗口内已经的packet均是待发送状态,此时只需要停止计时器,等待发送后启动计时器
注意这期间只有唯一的计时器,该计时器在窗口移动时重新记时
发送方FSM与接受方FSM:
纠正下图的"如果下一个分组未发送" “如果窗口内的包均被确认base == nextsequm,则停止计时器,此时窗口内均是未发送的包,见下图 ,否则说明窗口内还有发送但未确认的包,重开计时器”
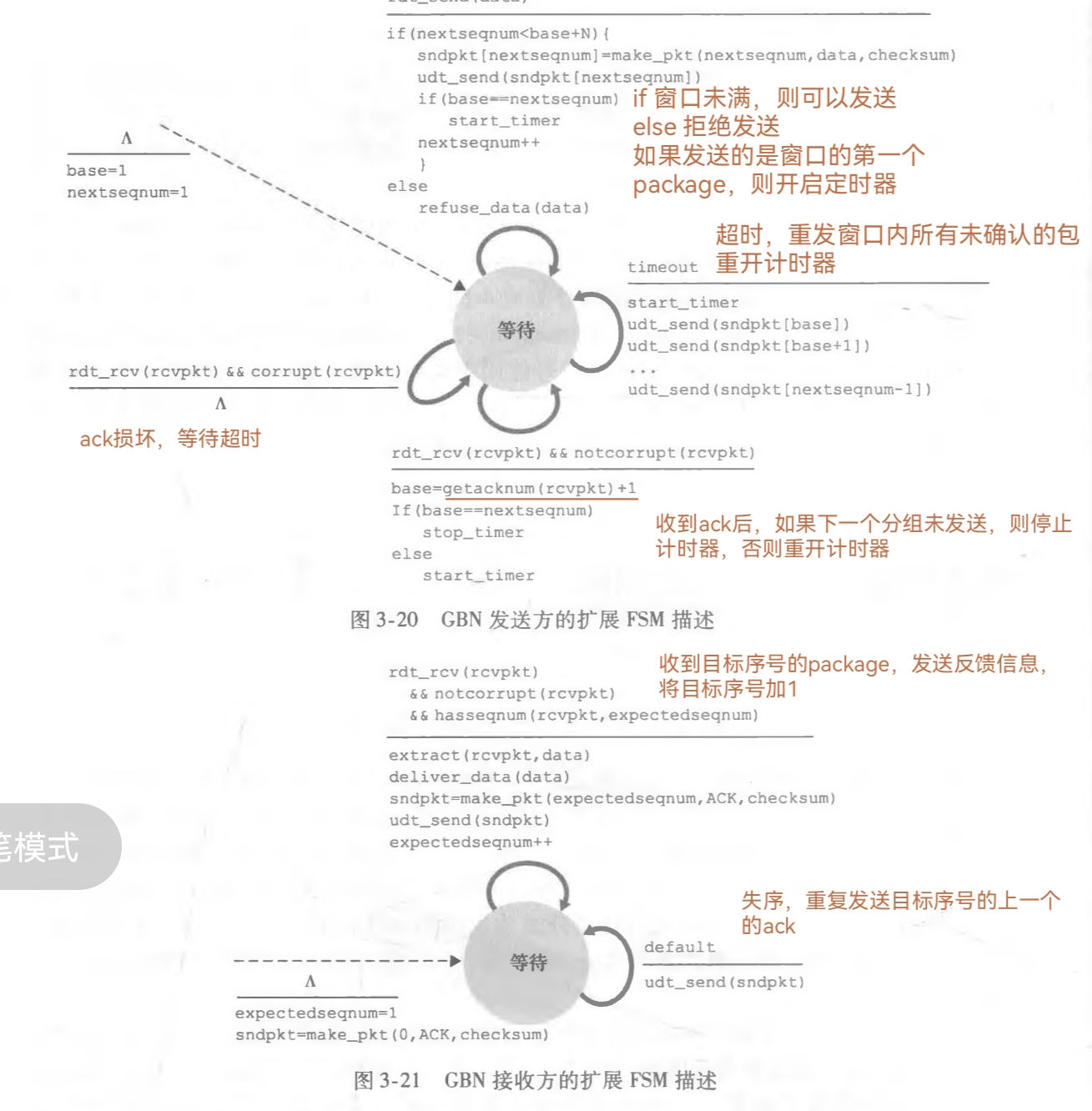
2.2 source code
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
/*******************************************************************
ALTERNATING BIT AND GO-BACK-N NETWORK EMULATOR: VERSION 1.1 J.F.Kurose
This code should be used for PA2, unidirectional or bidirectional
data transfer protocols (from A to B. Bidirectional transfer of data
is for extra credit and is not required). Network properties:
- one way network delay averages five time units (longer if there
are other messages in the channel for GBN), but can be larger
- packets can be corrupted (either the header or the data portion)
or lost, according to user-defined probabilities
- packets will be delivered in the order in which they were sent
(although some can be lost).
**********************************************************************/
#define BIDIRECTIONAL 0 /* change to 1 if you're doing extra credit */
/* and write a routine called B_output */
#define BUFFER_SIZE 50
const int N = 8; // window size of sliding-window protocol
int last_rev_seq; // last receiving packet seq in receriver B
int expected_seq; // expected packet sequence in receriver B
int base; // start seq of sending window in sender A
int nextseq; // next packet to be sent in the sending sliding window
/* a "msg" is the data unit passed from layer 5 (teachers code) to layer */
/* 4 (students' code). It contains the data (characters) to be delivered */
/* to layer 5 via the students transport level protocol entities. */
struct msg {
char data[20];
};
/* a packet is the data unit passed from layer 4 (students code) to layer */
/* 3 (teachers code). Note the pre-defined packet structure, which all */
/* students must follow. */
struct pkt {
int seqnum;
int acknum;
int checksum;
char payload[20];
};
struct pkt buffer[BUFFER_SIZE]; // buffer in sending A in order to retransmit
/* called from layer 5, passed the data to be sent to other side */
A_output(message) struct msg message;
{
if (nextseq >= base + N) {
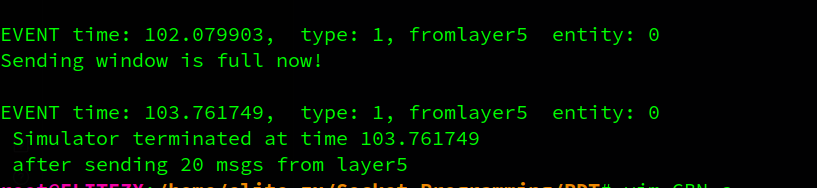
printf("Sending window is full now!\n");
return -1; // window is full
}
/* make pkt*/
struct pkt sndPkt;
sndPkt.seqnum = nextseq;
sndPkt.acknum = -1; // not a acknowledged packet
memcpy(sndPkt.payload, message.data, sizeof(message.data));
sndPkt.checksum = sndPkt.seqnum + sndPkt.acknum;
for (int i = 0; i < 20; ++i) sndPkt.checksum += sndPkt.payload[i];
printf("A is sending packet %d\n", nextseq);
buffer[nextseq] = sndPkt;
/*udt_send*/
tolayer3(0, sndPkt);
if (base == nextseq) // first packet of sending window, start timer
starttimer(0, 12.0);
++nextseq;
}
B_output(message) /* need be completed only for extra credit */
struct msg message;
{}
/* called from layer 3, when a packet arrives for layer 4 */
A_input(packet) struct pkt packet;
{
int tmp_checksum = packet.acknum + packet.seqnum;
if (tmp_checksum != packet.checksum) {
printf(
"ACK %d packet is corrupt! will timeout and retransmit all "
"packets in the sliding window!\n",
packet.acknum);
return -1;
}
if (packet.acknum < base) {
printf("duplicated ACK %d", packet.acknum);
return -1;
}
printf("ACK %d packet is not corrupt or duplicated! \n", packet.acknum);
/*base = getacknum(rcvpkt) + 1 */
base = packet.acknum + 1;
if (base == nextseq) // no packets sent in sliding window
{
printf("no packet sent in sliding window! stop timer! \n");
stoptimer(0);
} else // exist unacknowledged packet in the window
{
printf(
"The earliest sent packet is acknowledged, restart timer and move "
"sliding window!\n");
stoptimer(0);
starttimer(0, 12.0);
}
}
/* called when A's timer goes off */
A_timerinterrupt() {
/*Go Back N */
printf("Elite-zx: sender A GO BACK N, from packet %d to packet %d \n", base,
nextseq - 1);
for (int i = base; i < nextseq; ++i) {
tolayer3(0, buffer[i]);
}
starttimer(0, 12.0);
}
/* the following routine will be called once (only) before any other */
/* entity A routines are called. You can use it to do any initialization */
A_init() {
base = 0;
nextseq = 0;
}
/* Note that with simplex transfer from a-to-B, there is no B_output() */
/* called from layer 3, when a packet arrives for layer 4 at B*/
B_input(packet) struct pkt packet;
{
struct pkt ack_packet;
ack_packet.seqnum = packet.seqnum;
int tmp_checksum = packet.acknum + packet.seqnum;
for (int i = 0; i < 20; ++i) tmp_checksum += packet.payload[i];
if (tmp_checksum == packet.checksum && packet.seqnum == expected_seq) {
last_rev_seq = packet.seqnum;
++expected_seq;
printf("notcorrupt and expected packet %d! sending right ACK %d!\n",
packet.seqnum, last_rev_seq);
/*extract*/
struct msg extract_msg;
memcpy(extract_msg.data, packet.payload, sizeof(packet.payload));
/*deliver_data*/
tolayer5(1, extract_msg);
/* make_pkt*/
ack_packet.acknum = last_rev_seq;
ack_packet.checksum = ack_packet.seqnum + ack_packet.acknum;
tolayer3(1, ack_packet);
} else {
printf(
"corrupt or not expected packet %d (%d)! sending last receiving "
"ACK "
"%d!\n",
expected_seq, packet.seqnum, last_rev_seq);
ack_packet.acknum = last_rev_seq;
ack_packet.checksum = ack_packet.seqnum + ack_packet.acknum;
tolayer3(1, ack_packet);
}
}
/* called when B's timer goes off */
B_timerinterrupt() {}
/* the following rouytine will be called once (only) before any other */
/* entity B routines are called. You can use it to do any initialization */
B_init() {
last_rev_seq = -1;
expected_seq = 0;
}2.3. result
2.1 no loss and corruption
下面将分析部分输出来验证代码的正确性
A先发出两个packet,B对这两个packet进行了确认,A收到确认,窗口右移2次,此时窗口内没有已发送的包,因此暂停计时器。
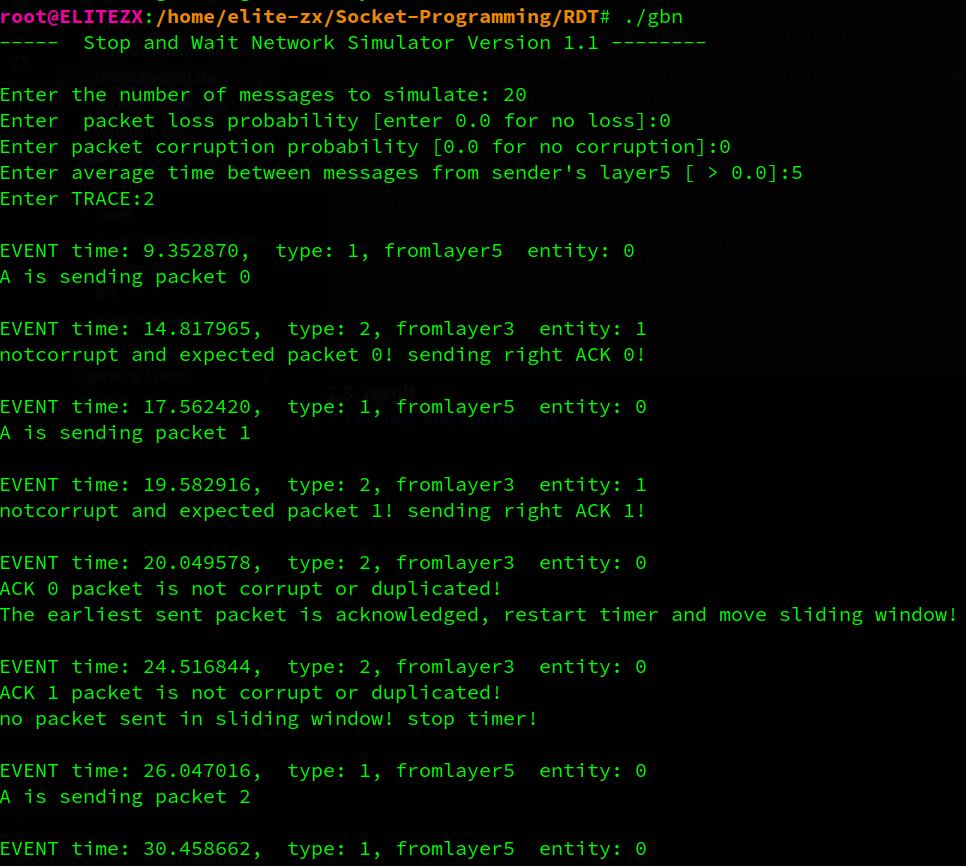
接着A发出packet2,3,4,B对这3个包逐一确认,但A在收到packet2的确认之前超时,A重传packet 2 to 4。B对packet2,3,4的ack到达A后,A移动窗口。B会收到冗余的packet 2,3,4,那么B会回复3个同样的ack 4信息,因为packet 4 是它最后收到的有序pkt。之后A会到收到冗余的ack4,A会打印说明自己收到了重复的ack信息。接着A继续发送packet5…
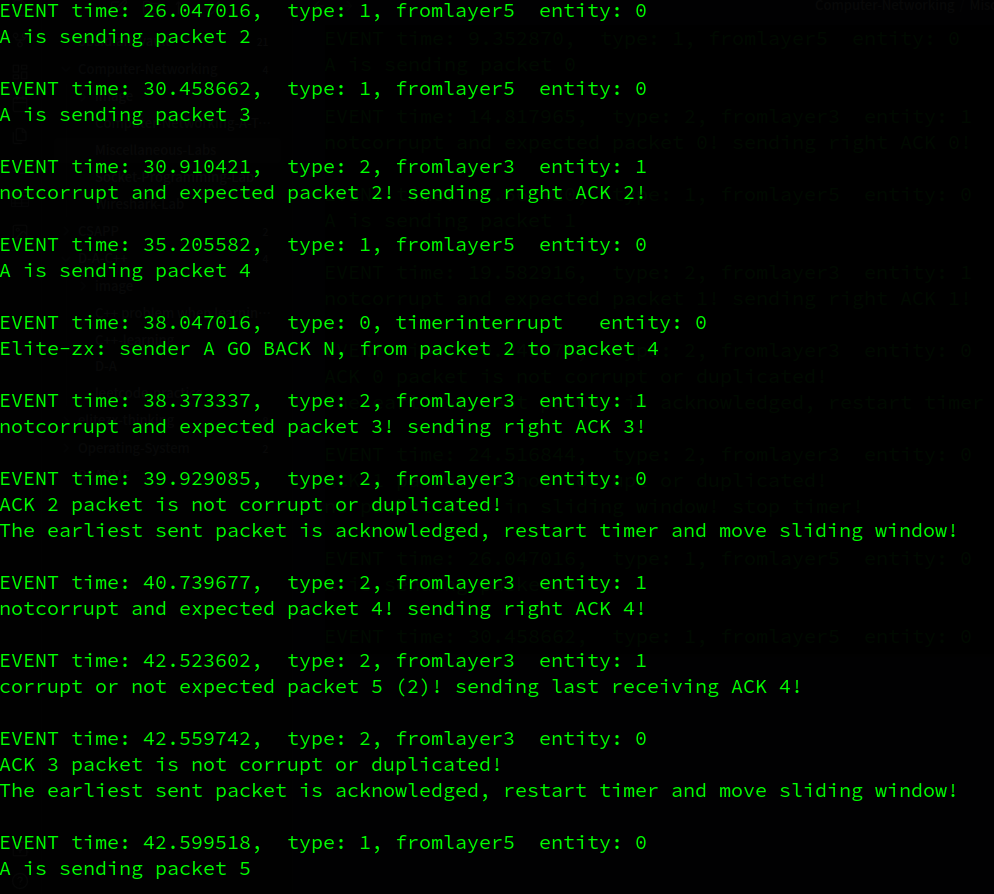
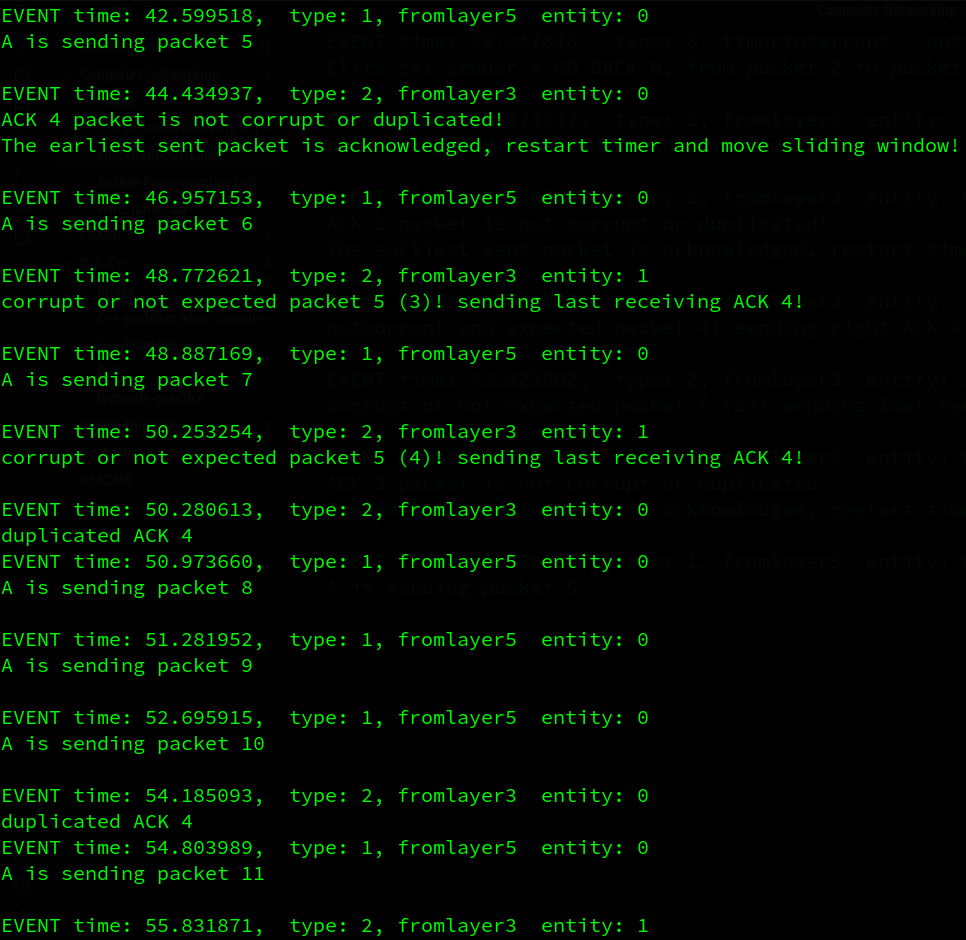
…
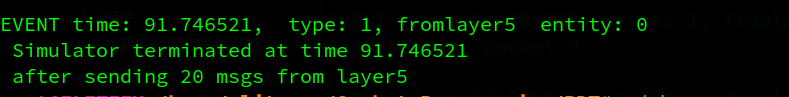
2.2. loss and corruption
下面将分析部分输出来验证代码的正确性
这里就简单说一下了。B对pkt 0的确认信息损失了,而此时A已经发出了0~2的pkt(其中pkt 1 丢失,pkt 2 损失), 因此A要超时重传pkt 0~2(pkt 2 损失), 因为B已经正确收到了pkt 0, 因此在收到冗余的pkt 0 时反馈ack 0, A成功收到ack 0 并移动窗口, 而B收到了重传的pkt1 而发送ack1信息…
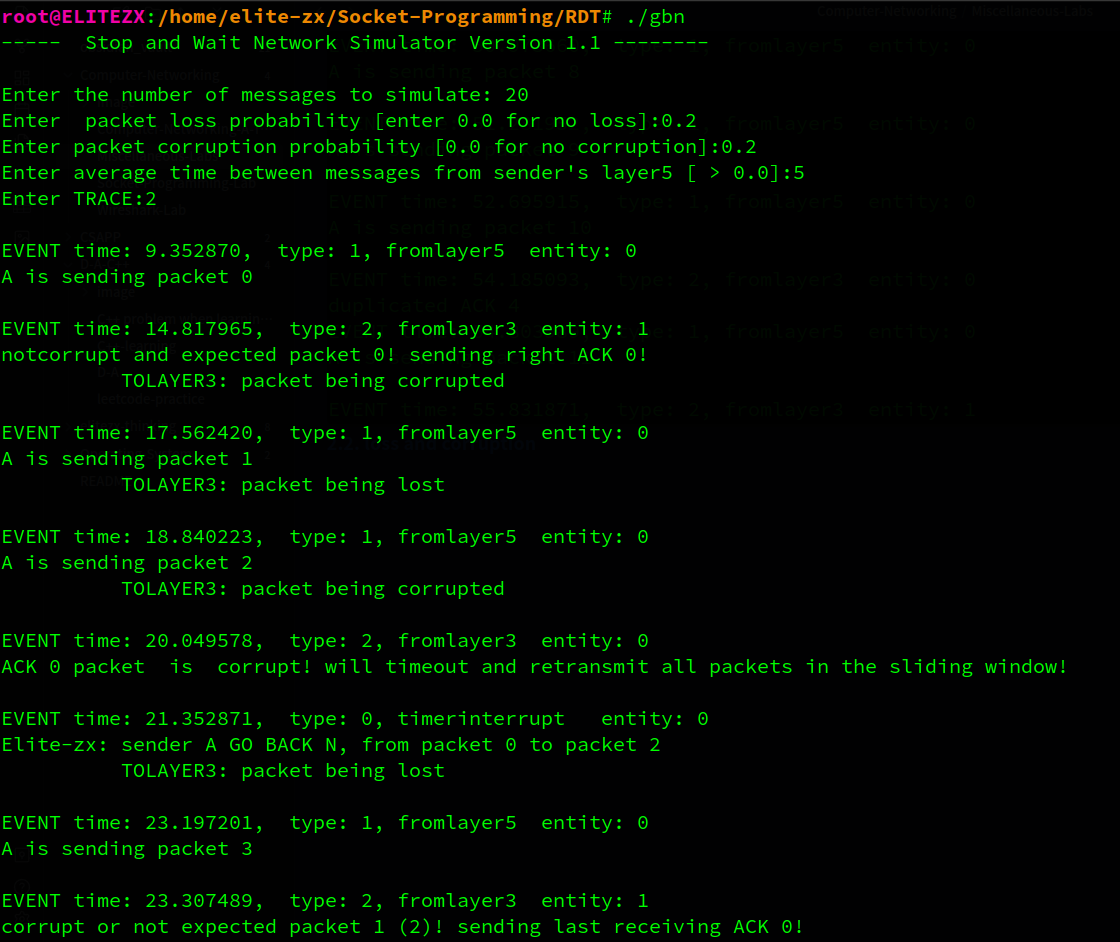
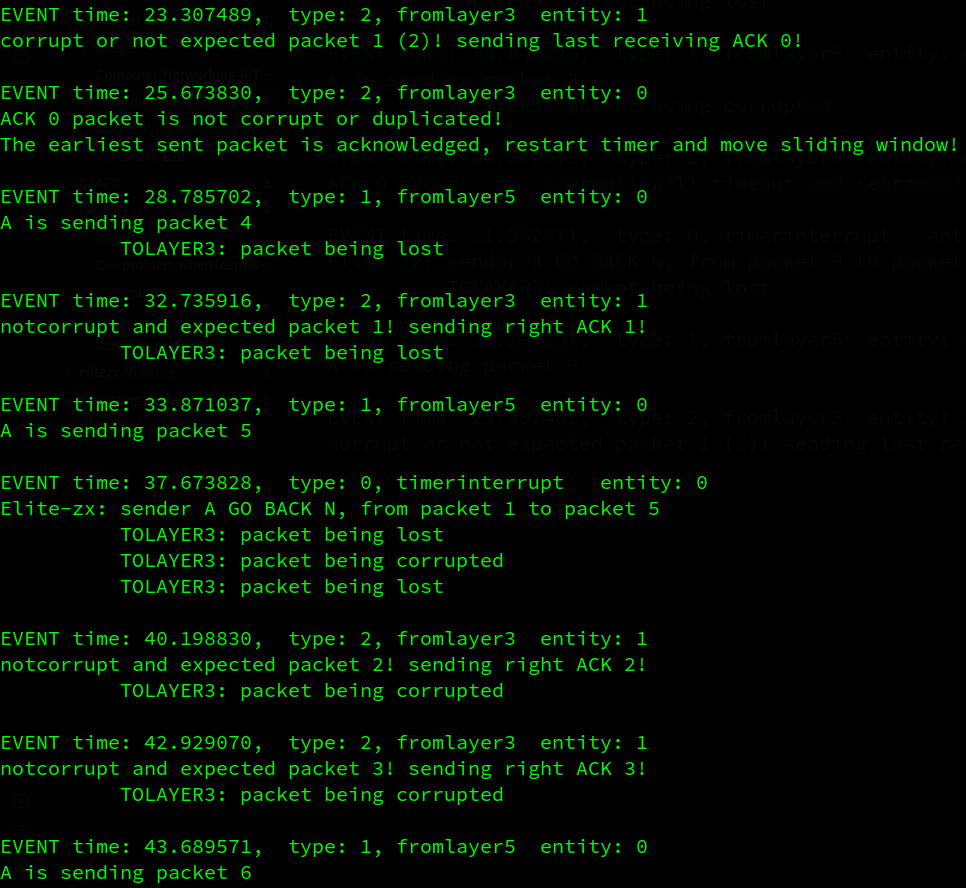
…